Imagine owning a self-sustaining setup where fish and plants live together symbiotically, benefiting not just each other, but you as well. Hidden amidst the hustle and bustle of urban chaos, this DIY Aquaponics system is a comprehensive amalgam of aquaculture and hydroponics, providing fresh, organic produce right in your backyard, all within your budget constraints. This passage aims to enlighten you on the diverse realms of Aquaponics, edifying you on the functional integrals, types – including the raft-based, media-filled bed, and nutrient film technique. You will gain insight into the necessary materials and tools requisite for the structure, locating cost-effective provisions, selecting the suitable tools and material, and illustrating recycling possibilities. Furthermore, we will guide you through the strategic designing of the system, covering aspects such as size, location, fish tank, grow bed, and pump & filter specifics. Lastly, the focus will shift on teaching you how to keep your Aquaponics system in check, ensuring an operative water parameter monitoring, sensible fish feeding techniques, plant pruning skills, and dealing with potential issues and diseases.
Understanding Aquaponics
Understanding Aquaponics: A Dive into the Basics
Aquaponics is a hybrid agricultural system which represents a symbiotic union between aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water without soil). The cycle begins with fish producing waste materials, primarily ammonia. Nitrifying bacteria residing in the system convert this ammonia into nitrites, then into nitrates, a form of nitrogen that plants can absorb and utilize. This process sanitizes the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish, and the cycle continues.
The benefits of using an aquaponic system are numerous. It’s a closed system, so it requires less water compared to traditional farming, making it ideal for drought-prone areas. It eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers because the nutrient-rich water from the fish tank provides all the essential nutrients that plants require, making it organic and eco-friendly. This method of farming also allows for densely packed plant growth without depleting soil nutrients since there is no soil involved.
The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants lies at the heart of the system: fish produce waste, which is converted to plant nutrients; plants, in turn, filter and clean the water for the fish, creating a closed, symbiotic cycle. Both parties provide essential services to its counterpart, thereby simulating a naturally occurring ecosystem.
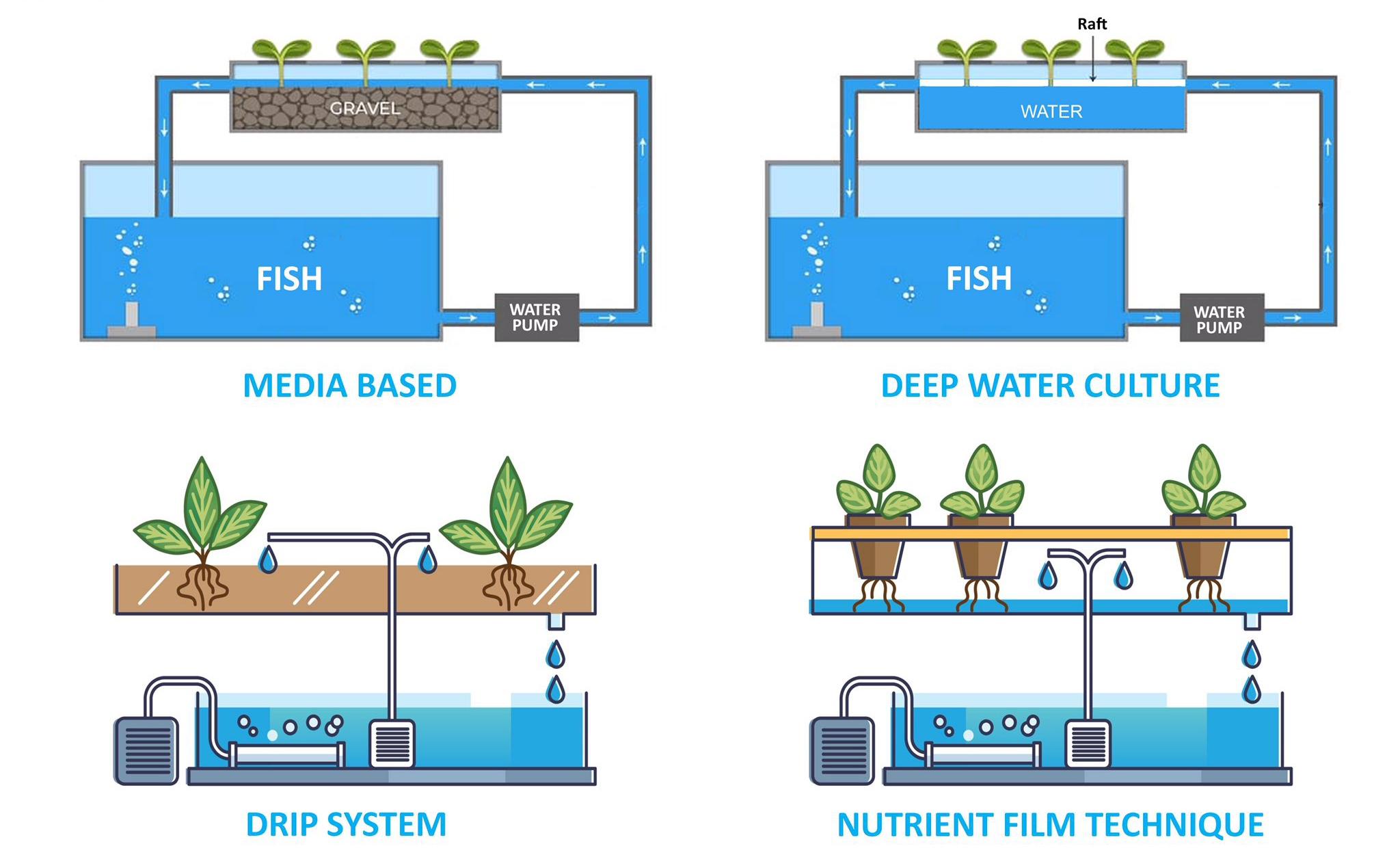
Types of Aquaponics Systems
There are several types of aquaponics systems, each with its unique set of advantages:
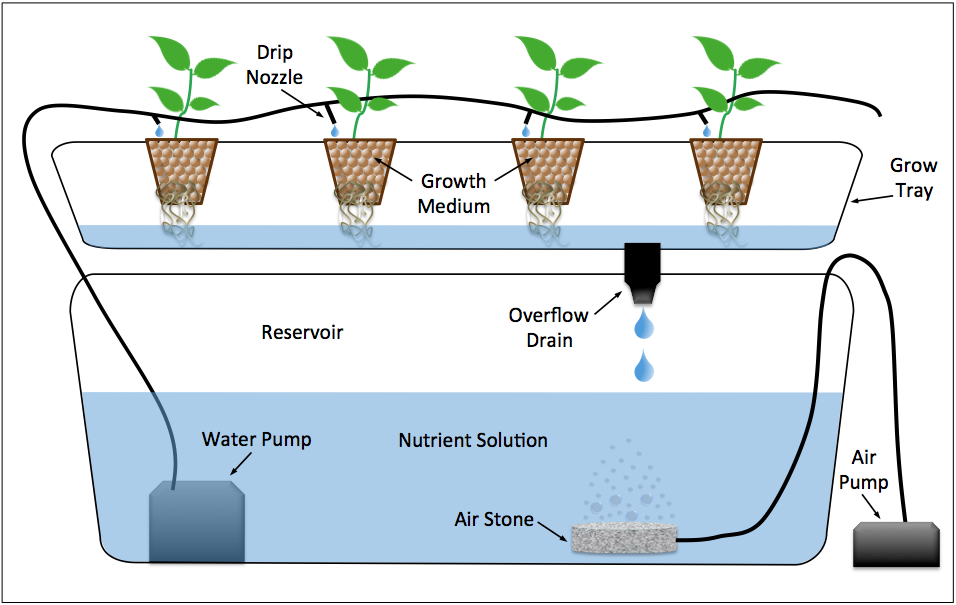
Materials and Tools Needed
Materials Needed for DIY Aquaponics System
To construct a DIY Aquaponics system on a budget, you’ll need a few basic materials. These include a fish tank, a growth bed (where your plants will grow), a water pump, an air pump, plumbing pipes, and fittings.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fish Tank | Any large, water-tight container. Consider repurposing a large plastic storage bin or investing in a cheap fish tank. |
| Growth Bed | Any large, shallow container. Materials that are food grade and can withstand long-term exposure to water are preferable. |
| Water Pump | An essential component for recirculating the water. Check our guide to filters and pumps for more information. |

Designing and Building the System
Planning the Layout
Before you start building your Aquaponics system, you’ll need to plan the layout and determine where each component will be placed. Considerations include:
- Size of the system
- Location (sunlight exposure, temperature, etc.)
- Type of fish and plants you intend to grow
- Accessibility for maintenance
You can find comprehensive guides on fish and plant selection as well as troubleshooting and maintenance on our website to help you make informed decisions.
Assembling the System
With the plan in place, it’s time to start assembling the system. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Set up the fish tank
- Build the grow bed
- Install the water and air pumps
- Connect the plumbing
- Add the fish and plants
- Monitor and maintain the system
Monitoring and Maintenance
Maintaining an Aquaponics system requires regular monitoring of water parameters such as pH, temperature, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates. Regularly checking these parameters ensures that both fish and plants are in a healthy environment.
Water Quality
Testing the water regularly is vital to the success of your Aquaponics system. Monitoring the pH levels, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels will ensure a thriving system. For more detailed information on water quality and filtration, check out our guide on filters.
Fish and Plant Health
Keep an eye on your fish and plants, ensuring they are growing healthy and are free from diseases. Regularly inspect for signs of stress or disease and take necessary actions. If you face any issues, consult our troubleshooting and maintenance guide.
Get Involved with Aquaponics Master
If you’re passionate about Aquaponics, consider joining our community for support, participating in events and workshops, or exploring Aquaponics products and kits.
For those who want to take a deeper dive into the world of Aquaponics, explore our advanced techniques and resources or incorporate Aquaponics into educational school projects.
Conclusion
Getting started with Aquaponics is an exciting journey that combines the best of aquaculture and hydroponics. With the right planning, tools, and guidance, you can create a thriving, sustainable, and eco-friendly system in your backyard or even indoors. Remember to consult our comprehensive guides and community resources as you embark on this rewarding venture. Happy farming!


